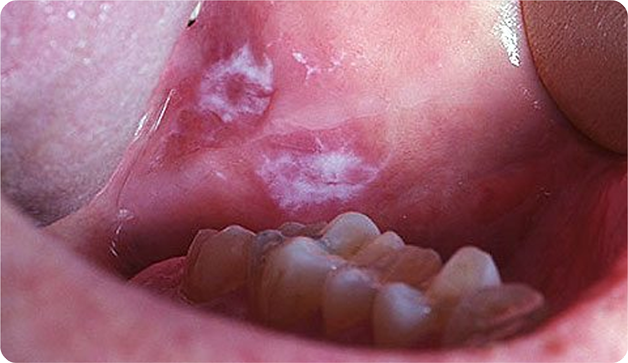
Mouth/Oral Cancer
Oral cancer is the second most prevalent cancer in India caused by excessive tobacco consumption and alcohol intake. In this type, cancerous cells develop in the lips, cheeks, tongue, floor of the mouth, soft and hard palate, throat, or sinuses. Some rare cancers can also develop in the salivary glands, tonsils, or pharynx.